Income Summary Definition, Purpose, How to Close
Unpack the Income Summary account’s purpose and process within financial accounting, linking revenues, expenses, and equity. It may be assumed that the income summary normal balance is on the credit side as this refers that the company expects the net income at the end of the period, in which it usually does expect that. When dividends are declared by corporations, they are usually recorded by debiting Dividends Payable income summary account and crediting Retained Earnings. Note that by doing this, it is already deducted from Retained Earnings (a capital account), hence will not require a closing entry. To close the drawing account to the capital account, we credit the drawing account and debit the capital account. Now for this step, we need to get the balance of the Income Summary account.
- Similarly, expense accounts, which typically have debit balances, are credited to bring their balances to zero.
- Our solution has the ability to prepare and post journal entries, which will be automatically posted into the ERP, automating 70% of your account reconciliation process.
- It is used to consolidate the balances of all revenue and expense accounts at the close of an accounting period.
- For net income, the Income Summary is debited to zero, and Retained Earnings is credited, increasing equity.
- The Income Summary will be closed with a debit for that amount and a credit to Retained Earnings or the owner’s capital account.
- Its primary function is to gather all revenue and expense balances at the end of an accounting period.
Automated Credit Scoring

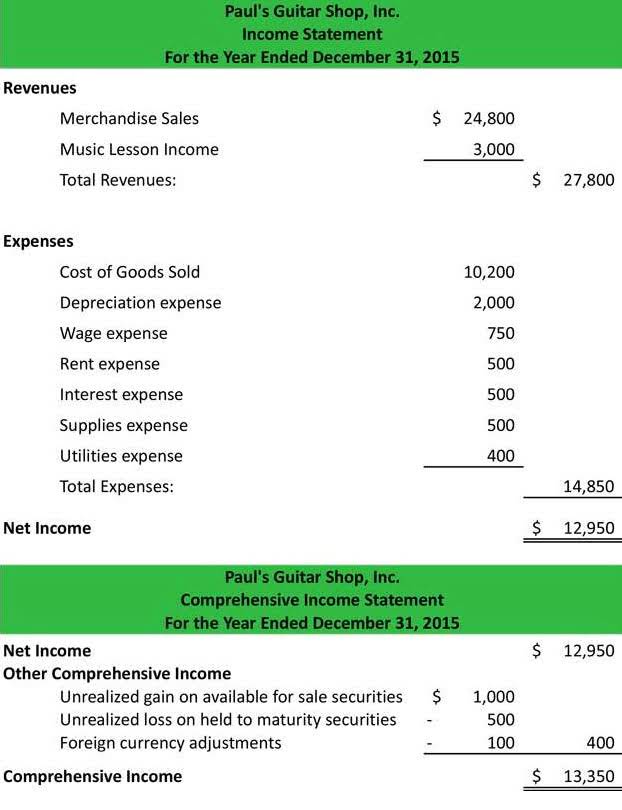
Learn about the Income Summary Account’s function in the accounting cycle, summarizing period results and facilitating financial reporting. This net balance of income summary represents the net income if it is on the credit side. On the other hand, if it is on the debit, it presents the net loss of the company. For partnerships, each partners’ capital account will be credited based on the agreement of the partnership (for example, 50% to Partner A, 30% to B, and 20% to C). For corporations, Income Summary is closed entirely to “Retained Earnings”. Let us understand the advantages of passing income summary closing entries for an organization or an individual through the points below.
In contrast, permanent accounts, or real accounts, carry their balances forward from one accounting period to the next. These accounts represent assets, liabilities, and equity, reflecting the ongoing financial position of a business. Examples of temporary accounts include all revenue accounts, expense accounts, and dividend or drawing accounts. Common permanent accounts include Cash, Accounts Receivable, Accounts Payable, and Owner’s Capital or Retained Earnings. The income summary account is an important part of the accounting cycle, specifically utilized during the closing process at the end of an accounting period. This process, often referred to as “closing the books,” is performed after financial statements have been prepared.
Company Overview
The income summary account is a temporary account used in the closing stage of the accounting cycle to collect the balances of the revenue and expense accounts, which are then closed. The purpose of the income summary account is to facilitate the process of closing temporary accounts and transfer their balances into the retained earnings account. To close these, the individual expense accounts are credited for their full balances, bringing them to a zero balance. The income summary account is then debited for the total amount of these expenses. After these steps, the income summary account will hold the combined total of all revenues as a credit and all expenses as a debit. If the credit balance is more than the debit balance, it indicates the profit; if the debit balance is more than the credit balance, it shows the loss.
Its function is to act as an intermediary, summarizing the financial performance of a business over a specific period by bringing together all revenue and expense figures. The income summary account serves as a temporary holding account in the accounting cycle. It is used to consolidate the balances of all revenue and expense accounts at the close of an accounting period. Its purpose is to facilitate the transfer of net income or loss into a permanent equity account, such as Retained Earnings, and to prepare temporary accounts for the next accounting period. The income summary account is a temporary account, meaning its balance is reset to zero at the end of each accounting period, typically a fiscal quarter or year. This contrasts with permanent accounts, such as assets, liabilities, and equity, whose balances carry forward from one accounting period to the next.
Close revenue accounts
Other approaches such as P&L Statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets can be used to analyze a company’s financial performance. If the Income Summary account has a credit balance and the revenue is greater than expenses, then it means the company has earned the net income. Otherwise, if the expenses are greater than revenue and there is a debit balance, the net loss has been incurred for the period 4.
- They zero-out the balances of temporary accounts during the current period to come up with fresh slates for the transactions in the next period.
- Once all individual revenue and expense accounts have been transferred into the Income Summary account, its balance will represent the net income or net loss for the period.
- If the Income Summary has a credit balance (net income), the Income Summary account is debited to zero it out, and Retained Earnings is credited to increase equity.
- The business has earned interest income of $8,000, revenues of $90,000, and miscellaneous income of $7,400.
- This transfers all incurred costs for the period into the summary account.
During the accounting period, you earned $5,000 in revenue and had $2,500 in expenses. Notice the balance in Income Summary matches the net income calculated on the Income Statement. If we had not used the Income Summary account, we would not have this figure to check, ensuring that we are on the right path.
Understanding the Income Summary Account
This serves as an excellent way for businesses to keep their financial records organized and start fresh each year. An income summary account is a temporary account used by businesses at the end of the year to organize their finances. At the end of the year, businesses gather all revenue and expenses and place them into an income summary account.

Temporary accounts are those that are closed at the end of an accounting cycle. Income summary effectively collects NI for the period and distributes the amount to be retained into retained earnings. Balances from temporary accounts are shifted to the income summary account first to leave an audit trail for accountants to follow. This final income summary balance is then transferred to the retained earnings (for corporations) or capital accounts (for partnerships) at the end of the period after the income statement is prepared. This income balance is then reported in the owner’s equity section of the balance sheet. For the rest of the year, the income summary account maintains a zero balance.
Income Summary Journal Entry
If the Income Summary has a debit balance, the amount is the company’s net loss. The Income Summary will be closed with a credit for that amount and a debit to Retained Earnings or the owner’s capital account. Next, if the Income Summary has a credit balance, the amount is the company’s net income. The Income Summary will be closed with a debit for that amount and a credit to Retained Earnings or the owner’s capital account. On the other hand, if the company makes a net loss, it can make the income summary journal entry by debiting retained earnings account and crediting the income summary account instead.
Income summary for expenses
They’d record declarations by debiting Dividends Payable and crediting Dividends. If this is the case, then this temporary dividends account needs to be closed at the end of the period to the capital account, Retained Earnings. Accounting tracks an organization’s financial health by systematically recording, summarizing, and reporting financial transactions. This process creates financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.